Overview
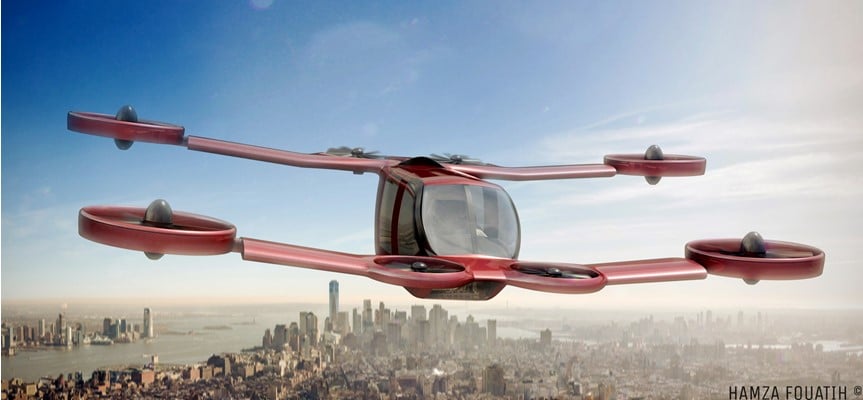
Mini-Bee is a vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft designed for urban air mobility. Here are some key technical features of the aircraft:
- Modular design: allows swapping between cargo, medevac or passenger roles.
- Electric propulsion: quiet and eco-friendly, with low maintenance needs.
- Hybrid system: onboard generator extends range for longer flights.
- Autonomous flight: advanced sensors and cameras for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- VTOL capability: no runway needed, perfect for urban deployment.
- High performance: 180 km/h top speed, 300 km range.
- Lightweight construction: carbon fiber and aluminum for better payloads.
Overall, Mini-Bee is a highly adaptable VTOL, ideal for multiple use cases in dense environments.

Collaborative project
This project is achieved under a dedicated Lesser Open Source License to foster open collaboration.
It welcomes academic, industrial, and independent contributors. Works are published via a shared public wiki under coordinator management.
Private or IP-protected tasks may also be included, with only interface deliverables covered by the open license. Participants retain the right to use outcomes for commercial or technical applications, with default royalty structures in place.
Key features
VTOL multicopters stand out for their vertical lift and compact versatility. Core traits include:
- Vertical Lift: Hover and land without runway infrastructure.
- Multirotor Design: Ensures flight control and balance.
- Electronic Stability: Onboard software keeps flights smooth.
- Autonomous Systems: Fully or semi-autonomous operation possible.
- Flexible Applications: From surveillance to aerial transport.
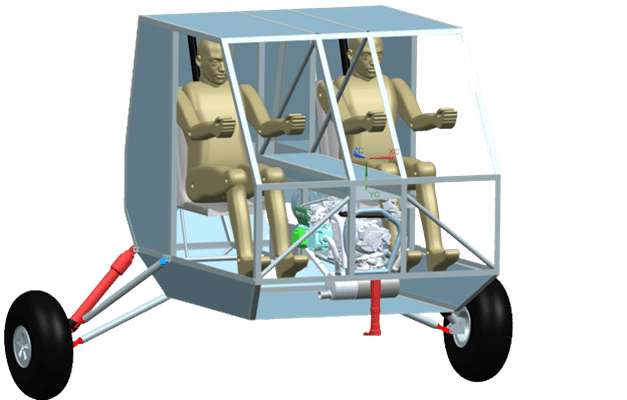
Specifications
The VTOL hybrid multicopter combines helicopter-style takeoff with airplane-like horizontal flight. To support this dual-mode capability, it includes specialized systems across propulsion, structure, and control.
Optimal Equipment
- Rotors: Multiple lifting rotors for precise vertical movement.
- Propellers: Supplementary thrust in horizontal flight.
- Sensors: GPS, IMU, barometers, and more for stable flight and auto-correction.
- Camera: Captures aerial views and facilitates situational awareness.
- Control System: Combines onboard electronics and pilot interface for real-time commands.
- Battery: High-density cells for electric power across systems.
- Communication: Ensures connection between UAV and operator via radio, WiFi, or mesh networks.
- Payload: Customizable depending on mission—medical kits, sensors, or cargo.
- Safety Features: Redundant systems, failsafe logic, and emergency shutdown routines.
Configure and Buy
- Rotor System: Multicopter rotors provide lift and agility.
- Engine: Powers systems and drives propulsion.
- Flight Controls: Stick, throttle, pedals—manual or digital control systems.
- Avionics: Navigation and communication electronics onboard.
- Landing Gear: Shock-absorbing legs or skids for safe ground contact.
- Fuel System: For hybrid units, ensures reliable power generation.
- Electrical System: Distributes energy across components.
- Instrument Panel: Displays altitude, airspeed, navigation data.
- Seats: Ergonomic placement for pilot or passengers as needed.
- Doors: Access for crew, patients, cargo—modular by design.
Each unit can be tailored to your specific use case—civilian, industrial, medical, or logistical. Get in touch to build your customized Mini-Bee configuration.

