The Evolution and Future of VTOL Technology: A Comprehensive Analysis
From Paul Cornu’s pioneering helicopter flight in 1907 to today’s fully electric vertical aircraft, VTOL technology has transformed how we imagine mobility. Marrying efficiency, sustainability, and innovation, VTOL aircraft are redefining the future of aviation—on land, in cities, and beyond.
Historical Milestones of VTOL Technology
- 1907 – Paul Cornu: Achieved the first free helicopter flight. Although short and unstable, it laid the foundation for vertical aviation.
- 1942 – Sikorsky R-4: The first mass-produced helicopter, proving VTOL could be practical.
- 1969 – Harrier Jump Jet: The first operational fixed-wing aircraft with vertical takeoff and landing using vectored thrust.
- 21st Century Surge: Innovations by Technoplane SAS, Airbus, and others have propelled VTOL into the mainstream with electrification and smarter materials.
Current State-of-the-Art VTOL Projects
Advanced VTOL Aircraft
- Airbus X3 / H160: Combining classic rotors with additional propulsion for increased speed and fly-by-wire control.
- Osprey V-22: A military-grade tiltrotor combining helicopter agility and airplane speed.
- Electric VTOL (eVTOL): Initiatives by Lilium, Joby Aviation, and Airbus E-Fan focus on silent, clean, short-range flights.
The Rise of Electric VTOL Technology
Electric propulsion is the beating heart of next-gen VTOL. eVTOL aircraft are designed for clean, efficient short-distance flights, ideal for city commutes and cargo drops. They rely on lithium-ion batteries or hybrid-electric systems to achieve sustainable lift-off.
Advantages of eVTOL Systems:
- Eco-friendly: No CO₂ emissions, meeting climate goals.
- Affordable: Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts.
- Quiet: Reduced noise makes them ideal for urban use.
Key Technical Challenges:
- Battery Tech: Limited range due to low energy density. Batteries also increase weight significantly.
- Thermal Management: Heat buildup from propulsion systems must be managed for safety.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Certification standards from FAA and EASA are still emerging for eVTOL aircraft.
- Urban Infrastructure: Building efficient “vertiports” is essential for deployment in cities.
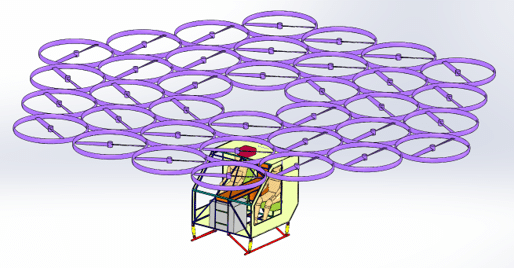
Emerging Trends in VTOL Development
- Autonomous Navigation: AI systems and sensor fusion are enabling safe, pilotless VTOL flights.
- Hybrid Platforms: Mixing combustion and electric for better range during battery evolution.
- Urban Air Mobility: Fleets of air taxis by Uber Elevate, Lilium, and Volocopter are taking shape.
- Advanced Materials: Carbon-fiber and composites cut down weight while boosting strength.
Future Applications of VTOL Technology
From emergency care to logistics and defense, VTOL aircraft bring revolutionary flexibility to various sectors:
- EMS: Quick access to patients in hard-to-reach zones.
- Rescue: Navigate disaster areas with speed and precision.
- Delivery: Last-mile cargo made fast and aerial.
- Surveillance: Ideal for military, border patrol, and intelligence missions.
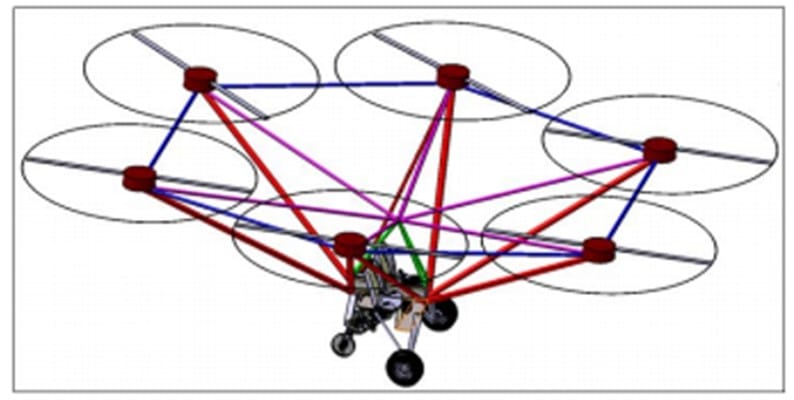
The Role of Model-Based Development in VTOL Engineering
Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE)
Designing VTOLs means managing complex systems. MBSE enables simulation, optimization of E/E systems, and faster certification—all in one smart workflow.
With tools from leaders like Siemens, teams can model, test, and validate designs from concept to flight-ready prototype—safely and efficiently.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for VTOL
From its humble beginnings in 1907 to today’s electric and autonomous aircraft, VTOL technology is reshaping the way we move, save lives, and deliver across the skies.
Thanks to innovators like Technoplane SAS and global aerospace leaders, we’re not just dreaming of a vertical future—we’re building it.
The future is vertical. The future is now.
